How 9 Enneagram types perceive decision making
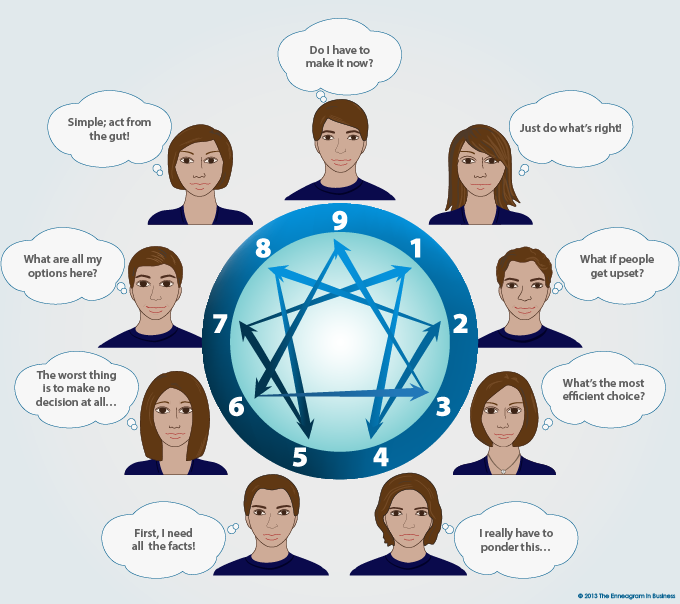
Decision Making and the Enneagram
People at all organizational levels – and especially leaders – make decisions large and small every day, and the cycle time for this has never been faster. At the same time, there is very little guidance for how to make optimal decisions, ones that have the greatest possible impact with the fewest repercussions.
The Enneagram’s decision-making application allows you to make well-founded decisions accessing your head, heart, and gut, but also taking into account the organizational culture, the organization’s decision-making expectations and authority structure, and other factors related to the decision such as its urgency, complexity, and the anticipated resistance.
Find out about the decision-making strengths, challenges and development tips for each Enneagram type.
Strengths
One
Trust their gut and use their mind to make sense of their gut reaction, operationalize decisions quickly
Two
Rely on their feeling sense and the impact on others, easily enlist others to follow their decisions
Three
Rapidly consider options with pros and cons of each, then move quickly to plans and action
Four
Make well-considered value-based decisions, often utilizing their intuition
Five
Use logical and thoroughly reasoned decisions, accessing all relevant facts
Six
Think through impact of all possible decisions, including possible scenarios that could become obstacles
Seven
Perceive multiple options for possible decisions, as well as a variety of pathways for execution
Eight
Make instantaneous, gut-based decisions that include big action and a systems understanding
Nine
Integrate varying viewpoints and alternatives using a 360-degree perspective, enlist others through consensus
Challenges
One
Quick reaction-based decision-making may result in not considering a variety of alternative choices
Two
May have difficulty making decisions that could generate resistance or negatively impact people
Three
May make decisions that are efficient or expedient but not necessarily effective
Four
May take a very long time to make important decisions, particularly when their values feel compromised
Five
Need abundant information, which may not be possible to obtain, to feel comfortable with a decision
Six
Become anxious – even paralyzed – making decisions, or may make impulsive ones
Seven
May make decisions too quickly based on a good idea, but without the deliberation needed
Eight
Make big decisions so quickly that other options not considered, or people not on-board with the action
Nine
Can feel extremely pressured when asked to make controversial or unilateral decisions
Development tips
One
Turn decision making into an art form, using just enough well-paced action to get the intended result
Two
Don’t let your personal feelings get in the way of making hard decisions, balance facts and feelings
Three
Use effectiveness, efficiency, and impact on people equally as your decision-making criteria
Four
Use logic, intuition, facts, and feelings equally in your decision-making deliberations
Five
Learn to make decisions faster by using your heart and gut as well as your head
Six
Trust yourself more by asking yourself what you would advise another to do in a similar situation
Seven
Make sure you have all the data, not just the highlights, before making your decisions
Eight
Question your assumptions before you take immediate action, slow down your process
Nine
Every time you need to make a decision, consult your gut and listen carefully


