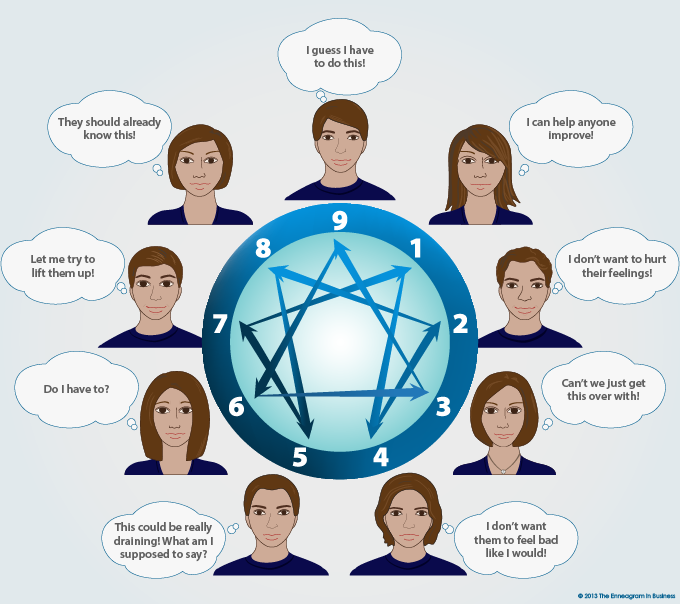
How the 9 Enneagram types perceive giving feedback
 Feedback and the Enneagram
Feedback and the Enneagram
Almost every person and every organization exist in a feedback deficit; people simply do not understand their impact on others or on their work and so they have to guess, often incorrectly, about their effectiveness. Most companies find it easier to train people than to offer them real-time positive and negative feedback, both of which can have a far deeper impact on a person’s behavior.
The Enneagram’s feedback application enables you to learn how to give effective feedback to others of the 9 types, as well as how to both use your Enneagram-based strengths and avoid the typical errors that go with your style when giving feedback to others.
Find out about the feedback strengths, challenges and development tips for each Enneagram type.
Strengths
One
Give highly specific feedback, with a deep desire to help others improve
Two
Offer feedback with warmth and support in such a way that others feel affirmed
Three
Provide honest and practical feedback given as a way to help others solve problems
Four
Give feedback with empathy, forethought and a desire to get to the deeper issues
Five
Offer concise, fact-based feedback in an objective way that does not feel overly personal
Six
Provide detailed, well-considered information that also contains consequences or impact
Seven
Give feedback with optimism, lightheartedness, and perspective
Eight
Offer honest, direct feedback focusing on the most essential points
Nine
Provide feedback with kindness, acceptance, and the ability to understand all viewpoints
Challenges
One
Using judgmental language or non-verbal indicators or pushing too hard to get improvement
Two
Being reluctant to give negative feedback or softening negative feedback so it doesn’t seem important
Three
Appearing impatient, overly focused, or not allowing sufficient dialogue about the topic
Four
Using too many personal stories or self-referencing language or being overly intense
Five
Hesitating to have a difficult conversation out of concern that it will become too emotional or draining
Six
Becoming overly anxious about giving the feedback and over-planned so the conversation is not relaxed
Seven
Being unwilling to offer negative feedback or to remain in the conversation until it is complete
Eight
Appearing intimidating or so in command such that the other person is reluctant to discuss or disagree
Nine
Offering the feedback in such a dispassionate way that the other person doesn’t take it seriously
Development tips
One
Offer as much positive as negative feedback, pay attention to your verbal and non-verbal cues
Two
Make sure your concern for the other person doesn’t limit your ability to be direct and clear
Three
Be gentle and clear simultaneously and be willing to engage in emotional conversations
Four
Make sure to be clear about your feelings versus those of the other person, reduce your intensity
Five
Speak from your heart as well as your head, spend the necessary time to process and discuss
Six
Be calm and clear before giving feedback, include the big picture as well as the details
Seven
Stay focused on your intention as well as the content you wish to offer, take your time
Eight
Be receptive to what the other person wants to say and encourage the dialogue
Nine
Be clear and focused while delivering the feedback in a direct way


